The Six Sigma is a tool designed to improve the quality of processes and the entire company. It is targeted, primarily, at searching for and eliminating the bottlenecks, and, secondarily, at facilitating to cut the cost of processes and increasing the profit.
SIX SIGMA
Statistical methods applied in process control were a baseline for Six Sigma. A new philosophy has been originated during development and combination of other quality tools. Nowadays, a complex and flexible entrepreneurial process how to achieve maximal business success of the company regards as Six Sigma. It is based on the understanding of the needs and expectation of customers, disciplined usage of information, data and statistical analyses. That all is used for controlled improvement of procurement, production, logistics and other processes.
Six Sigma proposes the following objectives:
- maximize profit
- market segment increase
- productivity increase
- cycle time reduction
- minimize of nonconformities, costs, mistakes and avoid its creation
- efficiency usage of resources
- successful control via processes monitoring
- and so on
Six Sigma tries to modify company processes in order to avoid negative phenomenon formation (loss, noncompliance, claims, etc.)
Basic principles explanation:
**Six Sigma** – methodology for processes and company quality improvement introduced by Motorola Company

Legal aspects of insolvency and reorganization

The Real | Interim Manager for Your Changes

Manager work model

Time management - making use of time effectively

Jak správně tvořit mapu procesů

Modelling and setting the processes and procedures - ISO 9001

Training - preparation of the SWOT analysis and strategy
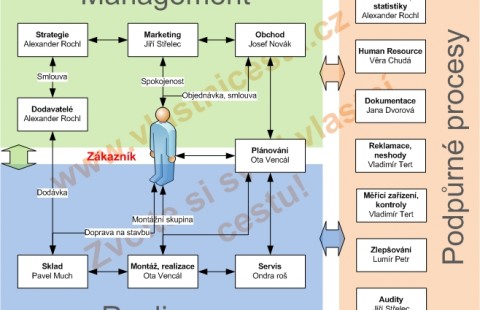
Company Management System of Quality Step by Step - ISO 9001
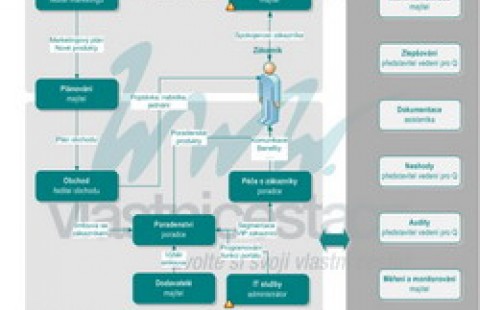
Process map acc ISO 9001 - business offer
**Sigma** - standard deviation of process’s characteristic, mainly used in SPC - Statistical Process Control). Deviation determines a range of variances or difference in selected group of items or selected process data.
**DPMO** – Defects Per Million Opportunities
**CTQ** – border limits critical to quality (Critical To Quality)
Six Sigma tools
Six sigma uses, during changes and creation of the company processes to the profit, plenty of tools you can know from the overall quality assurance and as well quality assurance according to ISO 9000 standard. As basic tools are:
1. Requirements and expectation of customer
2. Creative thinking
3. Process control
4. Statistical process control
5. Variability analyze
6. Balanced relations – people, processes, economics
7. Continual improvement
DMAIC model is used for Six Sigma implementation
DMAIC model is used for Six Sigma implementation, see picture, which originally comes from PDCA model. DMAIC model is more clear and complex and as well strongly feels a voice of customer and voice of processes.
Author, advisor "Jiří Střelec":http://www.ownway.eu/jstrelec/
